Pcolor
pcolor(X, Y, C::Matrix{<:Real}; kwargs...)Creates a colored cells plot using the values in matrix C. The color of each cell depends on the value of each value of C after consulting a color table (cpt). If a color table is not provided via option cmap=xxx we compute a default one.
Args
X,Y: Vectors or 1 row matrices with the x- and y-coordinates for the vertices. The number of elements ofXmust match the number of columns inC(is using the grid registration model) or exceed it by one (pixel registration). The same forYand the number of rows inC. Notice thatXandYdo not need to be equispaced.X,Y: Matrices with the x- and y-coordinates for the vertices. In this case the ifXandYdefine an m-by-n grid, thenCshould be an (m-1)-by-(n-1) matrix, though we also allow it to be m-by-n but we then drop the last row and column fromCC: A matrix with the values that will be used to color the cells.
Kwargs
This form of pcolor is in fact a wrap up of $plot$ so any option of that module can be used here.
labels: If this $keyword$ is used then we plot the value of each node in the corresponding cell. Uselabel=n, where $n$ is integer and represents the number of printed decimals. Any other value like $true$, $"y"$ or $:y$ tells the program to guess the number of decimals.font: Whenlabelis used one may also control text font settings. Options are a subset of the $text$attriboption. Namely, the angle and the $font$. Example: $font=(angle=45, font=(5,:red))$. If not specified, it defaults to $font=(font=(6,:black),)$.
D = pcolor(X, Y; kwargs...)This form, that is without a color matrix, accepts X and Y as before but returns the tiles in a vector of GMTdatasets. Use the kwargs option to pass for example a projection setting (as for example $proj=:geo$).
pcolor(G::GMTgrid; kwargs...)This form takes a grid (or the file name of one) as input an paints it's cell with a constant color.
outline: Draw the tile outlines and specify a custom pen if the default pen is not to your liking.kwargs: This form ofpcoloris a wrap of $grdview$ so any option of that module can be used here. One can for example control the tilling option via $grdview's$ $tiles$ option.
pcolor(GorD; kwargs...)If GorD is either a GMTgrid or a GMTdataset containing a Pearson correlation matrix obtained with $cor()$, the processing recieves a special treatment. In this case, other than the labels keyword, user is also interested in seing if the automatic choice of x-annotaions angle is correct. If not, one can force it by setting the rotx (ot slanted) keywords.
Examples
# Create an example grid
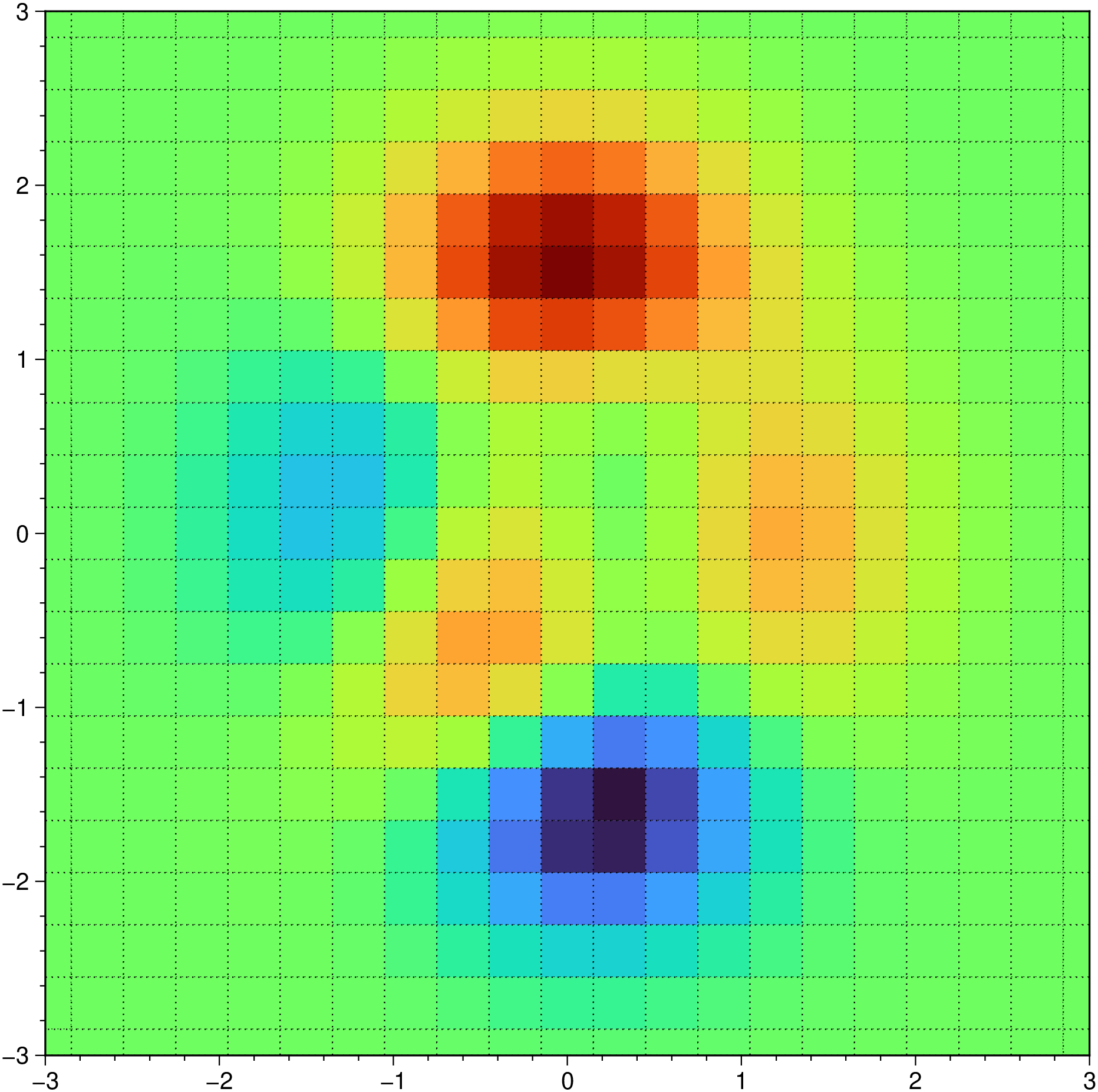
G = peaks(N=21);
pcolor(G, outline=(0.5,:dot), show=true)
# Now use the G x,y coordinates in the non-regular form
pcolor(G.x, G.y, G.z, show=true)
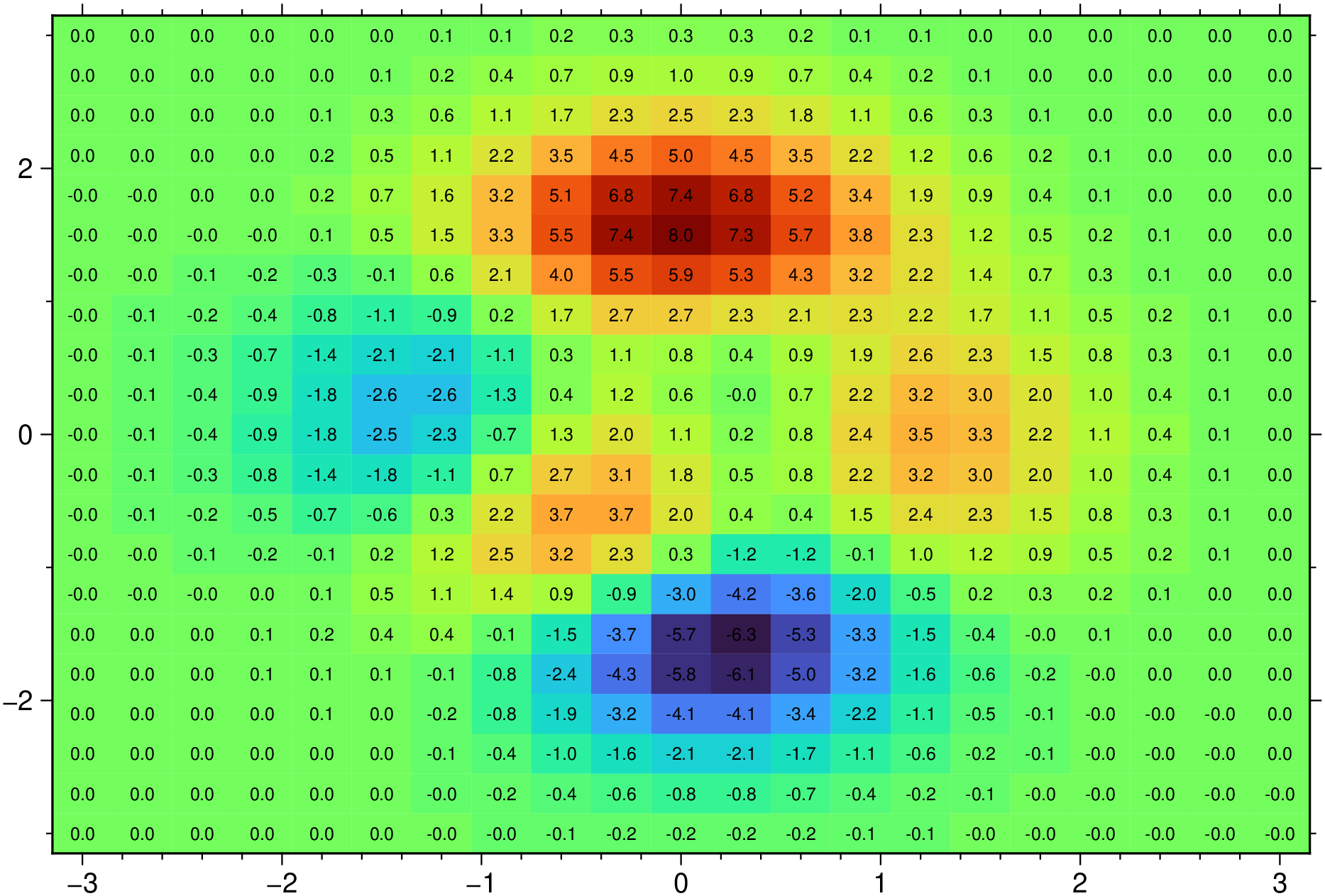
# Add labels to cells using default settings (font size = 6p)
pcolor(G.x, G.y, G.z, labels=:y, show=true)
# Similar to above but now set the number of decimlas in labels as well as it font settings
pcolor(G.x, G.y, G.z, labels=2, font=(angle=45, font=(5,:red)), show=1)
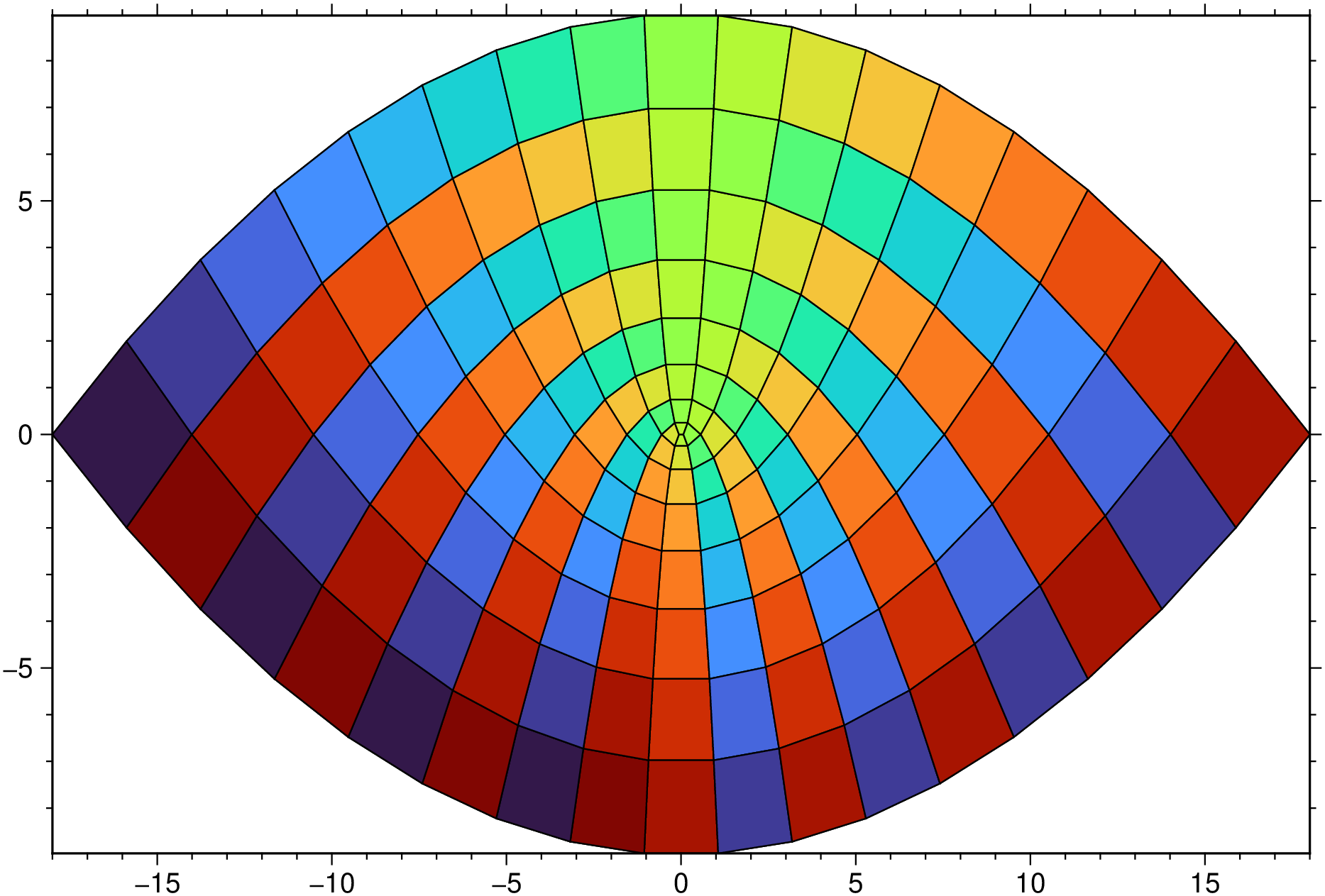
# An irregular grid
X,Y = meshgrid(-3:6/17:3);
XX = 2*X .* Y; YY = X.^2 .- Y.^2;
pcolor(XX,YY, reshape(repeat([1:18; 18:-1:1], 9,1), size(XX)), lc=:black, show=true)Display a Pearson's correlation matrix
pcolor(cor(rand(4,4)), labels=:y, colorbar=1, show=true)Rectangular grid
Create a pseudocolor plot with a rectangular grid.
using GMT
G = GMT.peaks(N=21);
pcolor(G, outline=(0.5,:dot), show=true)Rectangular grid with labels
using GMT
G = GMT.peaks(N=21);
pcolor(G.x, G.y, G.z, labels=:yes, show=true)Non-rectangular grid
Create a pseudocolor plot with a non-rectangular grid.
using GMT
X,Y = GMT.meshgrid(-3:6/17:3);
XX = 2*X .* Y;
YY = X.^2 .- Y.^2;
pcolor(XX,YY, reshape(repeat([1:18; 18:-1:1], 9,1), size(XX)), lc=:black, show=true)These docs were autogenerated using GMT: v1.33.1